Electromagnetic Crane Types

Electromagnetic overhead cranes are a staple in industries where precision and controlled material handling are paramount. These cranes feature powerful electromagnetic lifters suspended from an overhead structure, allowing them to lift and transport heavy loads with ease
Applications:
- Steel Mills: Used for precise movement of raw materials and finished products.
- Automotive Plants: Facilitate the assembly line process by handling heavy components.
Advantages:
- Precise control over lifting and positioning.
- Ideal for applications demanding accuracy and efficiency.
- Scrapyard Magnets (Electromagnets)
Scrapyard magnets, also known as electromagnets, are tailored for the efficient handling of ferrous scrap metal. These cranes utilize powerful electromagnetic forces to lift and move large amounts of metal, streamlining recycling processes.
Applications:
- Scrapyard Operations: Essential for lifting and moving ferrous scrap metal in recycling facilities.
- Metal Processing Plants: Used for efficient material handling in metal recycling.
Advantages:
- High lifting capacity for handling substantial metal loads.
- Contributes to the eco-friendly process of metal recycling.
- Electromagnetic Dock Crane
Designed for waterfront operations, electromagnetic dock cranes play a pivotal role in loading and unloading cargo from ships. These cranes utilize electromagnetic lifters to securely hold and transport containers, facilitating efficient port operations.
Applications:
- Ports and Harbors: Used for loading and unloading cargo containers from ships.
- Logistics Centers: Streamlining material handling in large shipping facilities.
Advantages:
- Speeds up loading and unloading processes in busy port environments.
- Capable of handling large and heavy cargo containers.
- Magnetic Levitation Crane
Magnetic levitation cranes, often referred to as maglev cranes, take electromagnetic technology to the next level by incorporating magnetic levitation for frictionless movement. These cranes hover above the ground, eliminating the need for wheels or tracks.
Applications:
- Clean Room Environments: Used in industries where minimizing contamination is crucial.
- High-tech Manufacturing: Ideal for delicate operations requiring precise and smooth movements.
Advantages:
- Frictionless movement reduces wear and tear on components.
- Well-suited for applications demanding a high level of cleanliness.
- Electromagnetic Coil Crane
Electromagnetic coil cranes utilize coiled electromagnetic components for lifting and transporting loads. These cranes are versatile and find applications in various industries where adaptability is essential.
Applications:
- Warehousing: Efficient handling of diverse loads in warehouse environments.
- Construction Sites: Versatile enough to handle different materials during construction projects.
Advantages:
- Versatility in handling a range of materials and load sizes.
- Adaptable to different operational requirements.
Electromagnetic Crane Drawing | Electromagnetic Crane Model


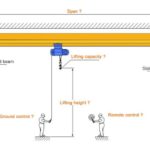
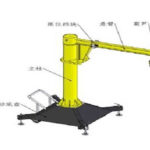
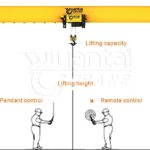
An electromagnetic crane consists of several essential parts that work together to lift and move heavy loads using electromagnetic principles. Here’s a breakdown of the main components:
Crane Structure:
The crane structure provides the framework and support for the entire system. It includes the vertical and horizontal beams, support columns, and other elements that contribute to the crane’s stability.
Electromagnetic Mechanism:
- Coil: The coil is a winding of wire through which an electric current passes. It is a crucial part of the electromagnetic system and generates a magnetic field when energized.
- Core: The core is typically made of ferromagnetic material and is placed within or around the coil. The magnetic field induced in the core enhances the strength of the electromagnetic force.
Lifting Mechanism: - Hook: The lifting hook is attached to the end of the crane’s hoist or lifting mechanism. It is used to connect and lift the load.
- Hoist Motor: The hoist motor provides the power to lift and lower the load. It is connected to the lifting hook through a system of gears and pulleys.
- Trolley: The trolley is a movable structure that runs along the horizontal beam of the crane. It supports the lifting mechanism and allows it to move horizontally, enabling the crane to position the load accurately.
Control System:
- Control Panel: The control panel contains the necessary controls for the crane operator to manage the crane’s movements. This may include buttons, switches, and a display for monitoring the crane’s status.
- Electrical Wiring: The electrical wiring connects the control panel to the electromagnetic mechanism and other electrical components, allowing the operator to send commands to the crane.
- Power Supply: Power Source: The crane requires a power source, typically electricity, to energize the electromagnetic coil and power the hoist motor.
Advantages of Electromagnetic Crane
- Precision and Control: One of the significant advantages of electromagnetic cranes is their ability to provide precise control during lifting and transporting operations. The electromagnetic lifters can be finely tuned to handle materials with accuracy, reducing the risk of damage and enhancing overall safety.
- Increased Productivity: The efficiency of electromagnetic cranes directly translates to increased productivity in various industries. Whether it’s in a steel mill, automotive plant, or scrapyard, the speed and precision of these cranes contribute to faster and more streamlined operations, ultimately boosting productivity and reducing downtime.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Electromagnetic cranes come with advanced safety features that make them reliable and secure for use in industrial settings. The electromagnetic lifters are designed to ensure a secure grip on materials, minimizing the risk of accidents or drops. Additionally, modern electromagnetic cranes often incorporate sensors and fail-safe mechanisms to further enhance safety during operation.
Applications of Electromagnetic Crane
- Steel Industry: The steel industry relies heavily on electromagnetic cranes for various tasks, from transporting raw materials within a facility to moving finished products. The precision and strength of electromagnetic lifters make them indispensable in steel mills, where heavy materials need to be manipulated with accuracy to ensure the quality of the final products.
- Automotive Manufacturing: In the automotive manufacturing sector, electromagnetic cranes play a vital role in the assembly line process. These cranes assist in the movement of heavy components, such as engines and chassis, ensuring a smooth and efficient production flow. The ability to precisely control the lifting and positioning of materials is crucial in maintaining the quality standards required in the automotive industry.
- Scrapyard Operations: As mentioned earlier, electromagnetic cranes, particularly scrapyard magnets, are extensively used in recycling facilities. These cranes efficiently lift and move large amounts of ferrous scrap metal, contributing to the recycling process. The magnetic force ensures a secure grip on the metal, preventing accidents and improving overall safety in scrapyard operations.